Have a great idea but not sure how to turn it into a product people will actually buy? Every successful product you see—whether it's a skincare line, a kitchen gadget, or a subscription box—started as just an idea in someone's head.
This guide breaks down the product development process into seven simple, beginner-friendly steps. Whether you're building something from scratch or improving an existing idea, these steps will help you go from inspiration to execution.
How to Create Products to Sell in 7 Key Steps
1. Identify a Real Problem
Before you create anything, it's important to know what problem your product will solve. When you solve a real problem, people are more likely to buy from you.
Why this matters: Your product needs to meet a real need, or it won't have much value to customers. Focus on something that frustrates or challenges people.
Practical tips:
- Talk to potential customers or friends to learn what annoys them.
- Use tools like Google Trends or Reddit to see what problems people discuss.
- Try surveys with platforms like SurveyMonkey to gather opinions.
Try this: Write down at least three problems you or others face daily and pick the one you feel most excited about solving.
Example scenario: Sarah started her skincare brand after noticing her friends complaining about sensitive skin products. She focused on gentle, natural ingredients to solve that problem, which helped her find loyal customers fast.
Further reading: 25 Best Niche for Dropshipping to Start a Profitable Store
2. Research Your Market and Competition
Understanding who else is selling similar products is key to making yours stand out. If you know what your competitors do well and where they fall short, you can create something better.
Why this matters: You don't want to waste time making a product nobody needs or that's already done perfectly.
Practical tips:
- Search for similar products on Amazon, Etsy, or niche websites.
- Read customer reviews to see what people like or hate about competitors.
- Use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs for deeper market research.
Try this: List the strengths and weaknesses of 3 competitor products and think about how your product can be different.
Example scenario: Mike launched a reusable water bottle after seeing complaints about leaks in existing designs. He improved the seal and got great reviews, beating some competitors.
Further reading: 11+ Low Competition Niches for Print on Demand: Best POD Niches
3. Define Your Product's Unique Selling Point (USP)
Your USP is what makes your product special and why customers should choose it over others. It could be quality, price, design, or something else unique.
Why this matters: A strong USP makes your product memorable and helps you market it better.
Practical tips:
- Write down what makes your product different in one clear sentence.
- Ask potential buyers if your USP makes sense to them.
- Test different USPs in small ads or social media posts to see what clicks.
Try this: Create a list of 5 features your product has and pick the top 2 that stand out most.
Example scenario: Emma's handcrafted jewelry stands out because she uses recycled metals, which appeals to eco-conscious buyers.
Further reading: How Many Listings Should I Have on Etsy to Boost Sales?
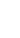
Source: Lumos Helmet
4. Design and Prototype Your Product
Turning your idea into a physical or digital prototype helps you see how it will actually work and look. This step is essential before full production.
Why this matters: A prototype shows flaws early, so you can fix them without big costs.
Practical tips:
- Use free design tools like Canva for digital products or SketchUp for physical ones.
- Try simple DIY versions at home or order prototypes from sites like Fiverr or Alibaba.
- Get feedback from friends or potential customers on your prototype.
Try this: Make a rough prototype using everyday materials or digital mockups to get a feel of your product.
Example scenario: John created a prototype of his phone stand using 3D printing. After testing it himself and with friends, he improved the angle and grip before selling it.
5. Test Your Product with Real Users
Testing your product with real users lets you find out what works and what doesn't from a customer's point of view.
Why this matters: Feedback helps you make your product better and avoid launching something no one wants.
Practical tips:
- Share samples or free versions in exchange for honest reviews.
- Use social media polls or groups to ask for opinions.
- Observe how users interact with your product and note issues.
Try this: Run a small beta test or focus group and gather detailed feedback.
Example scenario: Lisa gave her app to a group of friends and adjusted features based on their input, which improved the final version's user experience.
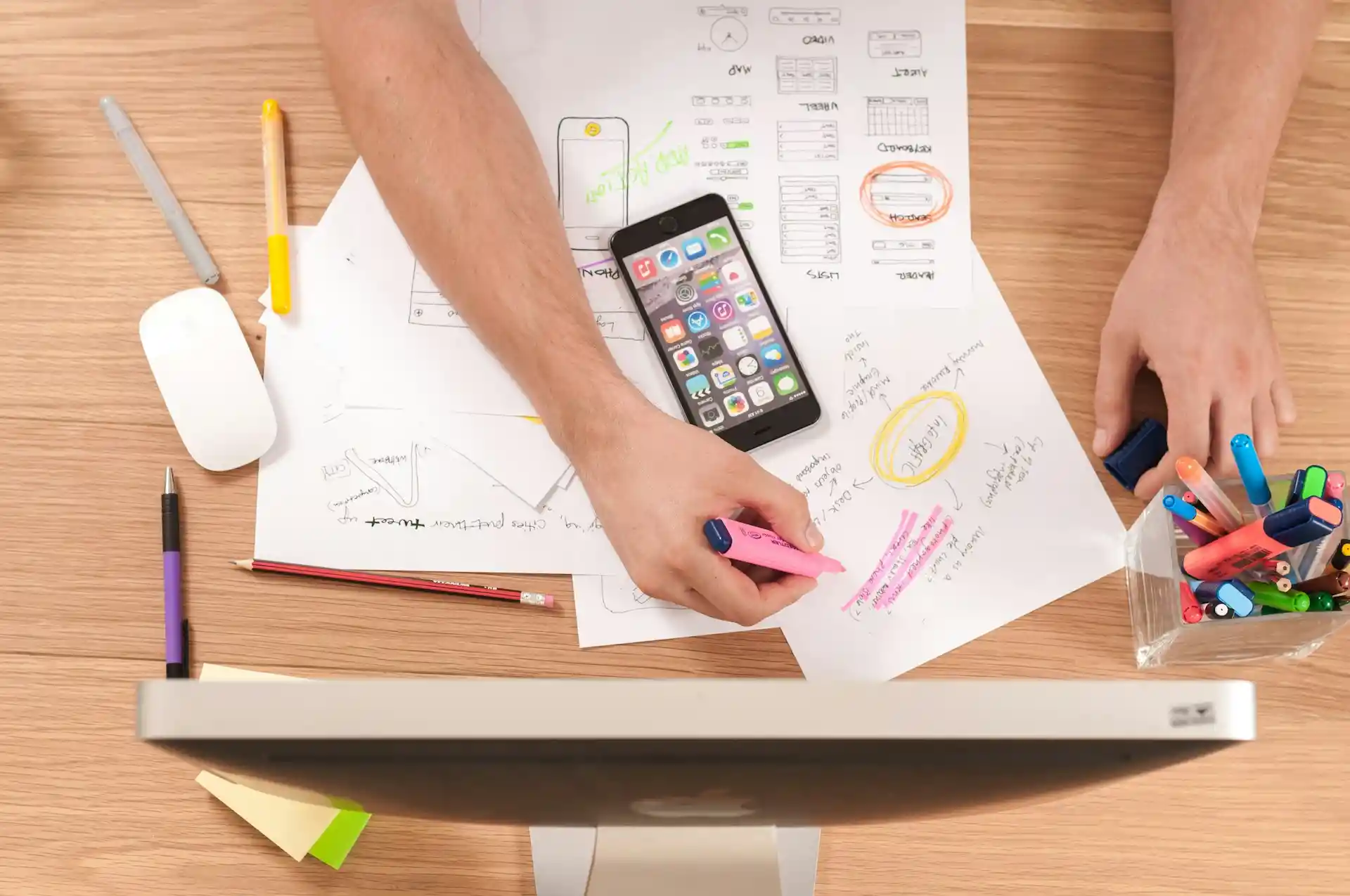

6. Plan Your Production and Pricing
Now that you know your product and customers well, figure out how to make it and at what price. Good planning saves money and ensures profit.
Why this matters: Without a clear production plan, costs can skyrocket and pricing may scare off buyers.
Practical tips:
- Contact several suppliers or manufacturers to compare costs.
- Use pricing calculators online to find the best price point.
- Consider your costs, desired profit, and what customers will pay.
Try this: Create a simple budget sheet to track production costs and expected selling price.
Example scenario: David negotiated with multiple factories for his t-shirts, choosing one with better quality and fair price, which helped him keep profits while staying competitive.
Further reading: How to Price Custom Shirts: Maximize Your Profit
7. Launch and Promote Your Product
Get your product out there. A good launch plan can create excitement and attract your first customers.
Why this matters: Even the best product won't sell if nobody knows about it.
Practical tips:
- Use social media platforms like Instagram or TikTok to show your product.
- Create a simple website or online store with Shopify or Etsy.
- Reach out to bloggers or influencers who fit your niche.
Try this: Plan a small online event or giveaway to build buzz around your product launch.
Example scenario: Rachel used Instagram Stories to share her handmade candles' making process, which drew attention and led to quick sales.
Further reading: How to Market Your Dropshipping Store: 16 Effective Ways
By following these steps, you're building a strong foundation for creating a product people want to buy. Take it one step at a time, and you'll see your idea come to life.
How to Find the Right Product Ideas to Sell
Finding the right product idea starts with identifying a real problem. When you focus on solving a problem, your product will naturally attract people who need it.
For example, think about something like excessive sweating. You can Google terms like "who suffers from excessive sweating" or "what excessive sweating is a sign of." This will help you find groups of people with this problem.
Maybe you choose pregnant women as your niche. Then, search for "how to deal with excessive sweating during pregnancy." This will give you ideas about products that could help.
Pick a product you are interested in or know something about. It's important because understanding the product will help you improve it. Read product reviews and forums to see what people complain about. This way, you learn how to make your product better.
Also, check the market size and competition. Look for ways your product can be different from others.
A good rule is to sell something you understand or would use yourself. This makes marketing easier because you know your customers well.
Tools, equipment, or devices are great ideas. They solve problems or help people work better and faster.
Keep in mind:
- Avoid very common products sold everywhere.
- Choose something with good profit margin.
- Make sure the product can ship easily.
Look around. What problems do you see? What products can help fix them? That's your starting point. Start simple. Start smart.
How to Prototype and Patent Your Product on a Budget
Starting with your product idea can feel confusing. You might have a rough version but don't know what to do next. The good news? You can build a better prototype without spending much.
Try rapid prototyping first. This means making quick, low-cost models to test your idea. You can use 3D printing or off-the-shelf electronics. Learning simple skills like soldering helps you build early versions without spending much.
If your product is mechanical, try free or cheap 3D design programs like OnShape. Print your design cheaply to see how it works. Don't rush to professional manufacturing before testing a few versions.

When it comes to patents, you can do a lot yourself. Filing a patent in the US is not expensive if you handle it. A design patent costs about $250, and you just need to fill out some forms.
There are two main types:
- Design patents protect how your product looks.
- Utility patents protect how it works.
Creating clear drawings of your product is the hardest part. But if you have a 3D model, use it to make your patent drawings easier.
Remember, the process is iterative. Build something. Show it to people. Get feedback. Then improve and repeat.
Auf diese Weise wissen Sie, dass Ihr Produkt wirklich ein Problem löst, bevor Sie mehr Geld oder Zeit investieren. Halten Sie es einfach, testen Sie oft und schützen Sie Ihre Idee klug.
DIY-Produkte vs. hergestellte Produkte zum Verkauf
Vorauszahlungskosten
Wenn Sie Produkte selbst herstellen, sind die initialen Kosten in der Regel niedrig. Sie kaufen nur das, was Sie benötigen, und vermeiden große Bestellungen.
Hergestellte Produkte erfordern jedoch oft ein größeres Budget, um in großen Mengen produziert zu werden.
Flexibilität und Design
DIY ermöglicht es Ihnen, Ihr Produkt jederzeit anzupassen und persönliche Details hinzuzufügen. Sie kontrollieren jeden Schritt.
Produktionsgeschwindigkeit und Volumen
Die Herstellung von Produkten von Hand dauert Zeit, was die Anzahl der Produkte, die Sie verkaufen können, begrenzt.
Die Herstellung ermöglicht eine schnellere, groß angelegte Produktion, sodass Sie mehr Kunden schnell bedienen können.
Konsistenz in der Qualität
Handgemachte Produkte können kleine Unterschiede zwischen den einzelnen Artikeln aufweisen.
Fabrikgefertigte Produkte sind in der Regel einheitlich, weil Maschinen genaue Spezifikationen befolgen.
Markengeschichte und Anziehungskraft
DIY-Produkte haben oft eine einzigartige, authentische Ausstrahlung, die von Kunden geschätzt wird.
Hergestellte Produkte können polierter und professioneller erscheinen, was einige Käufer bevorzugen.
Wenn Sie sich mehr auf das Wachstum Ihres Unternehmens konzentrieren möchten, kann die Herstellung Zeit sparen. DIY ermöglicht es Ihnen, direkt beteiligt zu sein, könnte jedoch Ihr Wachstum verlangsamen.
Aber ein Print-on-Demand-Anbieter kann Anpassungen und präzise Produktion nach Bedarf bieten und so das Beste aus beiden Welten kombinieren.
Beispiele für Produktentwicklung
Beyond Meat — Ethan Brown

Ethan Brown gründete Beyond Meat, weil er den Klimawandel bekämpfen wollte, indem er pflanzliche Fleischalternativen anbot.
Er arbeitete mit zwei Professoren der University of Missouri zusammen, die eine Technologie entwickelt hatten, um die Textur von Fleisch mit pflanzlichen Proteinen nachzuahmen. Brown lizenzierte ihre Technologie und gründete Beyond Meat im Jahr 2009.
Brown konzentrierte sich auf pflanzliches Rindfleisch und brachte 2015 den Beyond Burger auf den Markt. Dieses Produkt verwendet Erbsen-, Reis- und Linsenproteine sowie Rote-Bete-Saft, um die Blutfarbe nachzuahmen.
Eine große Herausforderung war es, das pflanzliche Fleisch so überzeugend zu machen, dass auch Fleischliebhaber gewonnen werden konnten. Aber durch ständiges Testen und Verbesserungen wurde Beyond Meat eine Marke, die für realistische und schmackhafte Produkte bekannt wurde.
Ihre einfache, moderne Verpackung unterstützt den Fokus der Marke auf Nachhaltigkeit und Innovation.
Lumos Ultra in Fahrradhelmen — Lumos Helmet
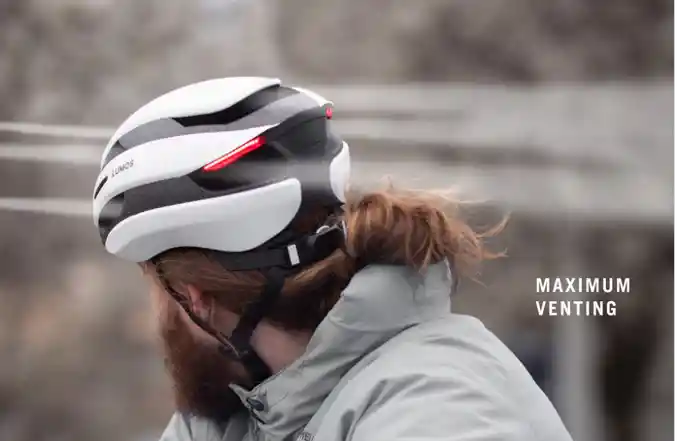

Quelle: Lumos Helmet
Lumos Helmet entwickelte den Lumos Ultra Fahrradhelm, weil sie bemerkten, dass Radfahrer einen sichereren, intelligenteren Helm benötigten, der auch gut aussieht.
Sie wollten einen Helm mit hellen LED-Lichtern, Blinkern und zusätzlichen Sicherheitsfunktionen in ein schlankes Design integrieren.
Um dies zu erreichen, testeten sie drahtlose Steuerungen, einschließlich einer, die Sie mit einer Apple Watch bedienen können. Sie konzentrierten sich auch darauf, den Helm leicht und gut belüftet zu gestalten und ihn gleichzeitig wasserdicht für alle Wetterbedingungen zu machen.
Eine der größten Herausforderungen war es, Gewicht und Sicherheit auszubalancieren, aber sie schafften es, den Helm leichter zu machen, ohne den Schutz zu verlieren.
Dank dieser Funktionen haben 24.943 Unterstützer 2.966.439 $ beigetragen, um das Projekt auf Kickstarter zu realisieren.
Der Lumos Ultra hilft Ihnen, sichtbar und sicher auf der Straße zu bleiben, während er mit seinen leuchtenden Farben und dem smarten Design Stil verleiht.
Expertentipps
Jetzt, da Sie die wichtigsten Schritte zum Erstellen von Produkten zum Verkauf gelernt haben, sind Sie bereit, Ihre eigene Reise zu beginnen. Denken Sie daran, jedes Produkt beginnt mit einer klaren Idee und dem Verständnis dafür, was die Menschen brauchen. Sie werden Ihr Produkt Schritt für Schritt entwerfen, testen und verbessern.
Mit Geduld und Einsatz können Sie Ihre Idee in etwas verwandeln, das die Menschen kaufen möchten. Also nehmen Sie, was Sie gelernt haben, glauben Sie an sich selbst und beginnen Sie mit dem Aufbau.
FAQs
Was kann ich zu Hause herstellen und verkaufen?
Erstellen Sie handgemachte Artikel wie Kerzen, Schmuck oder Gebäck. Digitale Produkte wie Druckvorlagen oder Online-Kurse funktionieren auch. Wählen Sie etwas, das Sie gerne herstellen und das einen Kundenbedarf deckt.
Ist es besser, digitale Produkte oder physische Produkte zu verkaufen?
Digitale Produkte wie E-Books sind leicht skalierbar mit niedrigen Kosten. Physische Produkte wie Handwerkskunst fühlen sich greifbar an, benötigen aber Versand. Wählen Sie basierend auf Ihren Fähigkeiten und den Vorlieben der Kunden.
Was ist ein Minimum Viable Product?
Ein Minimum Viable Product ist eine einfache Version Ihrer Idee, die Sie mit Kunden testen können. Es hat die Kernfunktionen, um schnell Feedback zu erhalten und Ihnen zu helfen, sich vor einer vollständigen Markteinführung zu verbessern.
Was sind die besten Plattformen, um Produkte zu verkaufen?
Verwenden Sie Etsy für handgemachte Waren, Shopify für benutzerdefinierte Stores oder Gumroad für digitale Produkte. Soziale Plattformen wie Instagram eignen sich ebenfalls, um Käufer direkt mit Ihren Kreationen zu erreichen.








 Global Shipping
Global Shipping








 Made in USA
Made in USA